A distinction is made between cooled and uncooled IR imagers. Cooled IR imagers work according to the internal photoelectric effect and are usually used with an expensive Stirling cooler. In comparison, the uncooled microbolometer arrays are operated at room temperature and used as low-cost IR imagers in thermal imaging cameras. Nowadays, the uncooled IR imagers have also reached a sensibility through the development and manufacturing processes from microsystem technology that was previously only possible with cooled IR imagers. The application areas of these low-cost IR imagers have thus been extended.
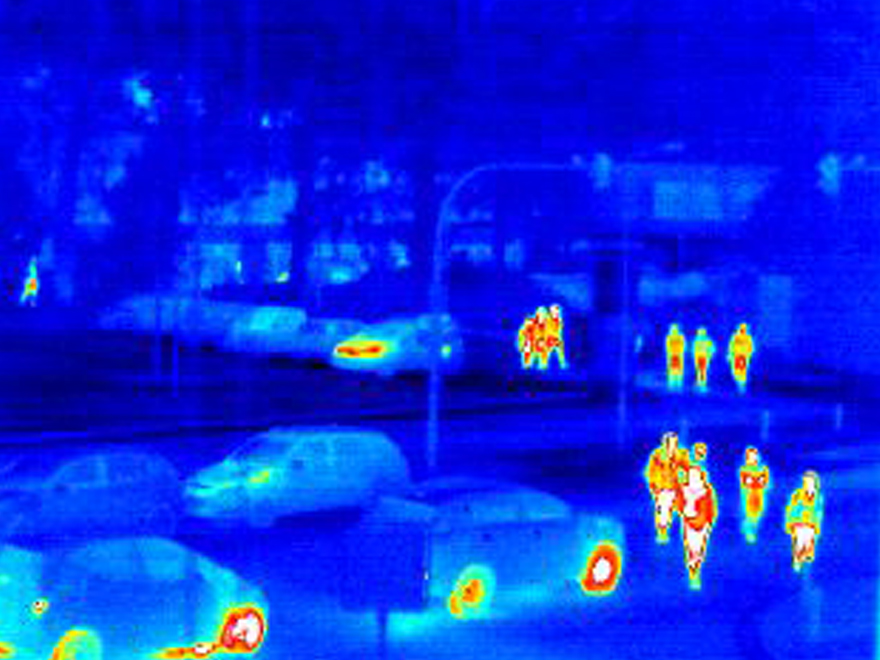
The thermal imaging camera as a typical system with IR imager can be used in many different fields of application. With its help the surface temperature can be determined contactless by means of the infrared radiation emitted by the object. The original application for IR imagers lies in the military sector and is target recognition in darkness or in poor visibility. The common field of application in the civil sector is imaging thermography for building inspection, in which the thermal insulation of buildings is examined and evaluated.
With the growing range of inexpensive uncooled IR imagers, many other fields of application have opened up in addition to the classic applications. While cooled systems continue to take an important position in the military sector, uncooled systems have also opened up their own applications. They show their advantages through their more compact design and their energy-efficient and low-maintenance operation. The civil sector, on the other hand, is largely dominated by the more cost-effective uncooled IR imagers. In the automotive sector they are used from driver assistance systems to autonomous driving. They offer safe, continuous and reliable detection of the environment, people and animals, especially in darkness and difficult visibility conditions.
In medical technology the measurement of temperature distribution and reaction of the human body can be used as a non-invasive and gentle method for the detection of diseases. In agriculture, the condition of plants can be observed, e.g. by observing their supply of water or also the health of animals. Temperature is an important parameter in many technological processes. Since this cannot always be measured directly, thermography is used for non-contact temperature measurements as an important component in process development, control and quality assurance.
Further details and more applications can be found down below