
In addition to common imaging thermography, there are many fields for application-specific IR imagers. The special requirements for IR imagers can refer to, for example, the temperature range in observation or the optical resolution. Due to insufficient reasonable economic alternatives, commercially available thermography cameras or infrared cameras are often used for these purposes. However, there are many applications in which the use of standard far-infrared sensors don’t deliver a sufficient performance. Many application-specific IR imagers are used for monitoring or controlling of temperatures in a comparatively high range (> 900 °C) in the glass and metal industry. Here, the emitted electromagnetic radiation is more in a medium (MWIR) instead of a far-infrared range (LWIR). Commercially available uncooled IR imagers are usually equipped with optical filters that block IR radiation below 7 μm wavelength. Therefore, there is only a small part of the radiation available to these IR imagers to determine the temperature at high object temperatures.
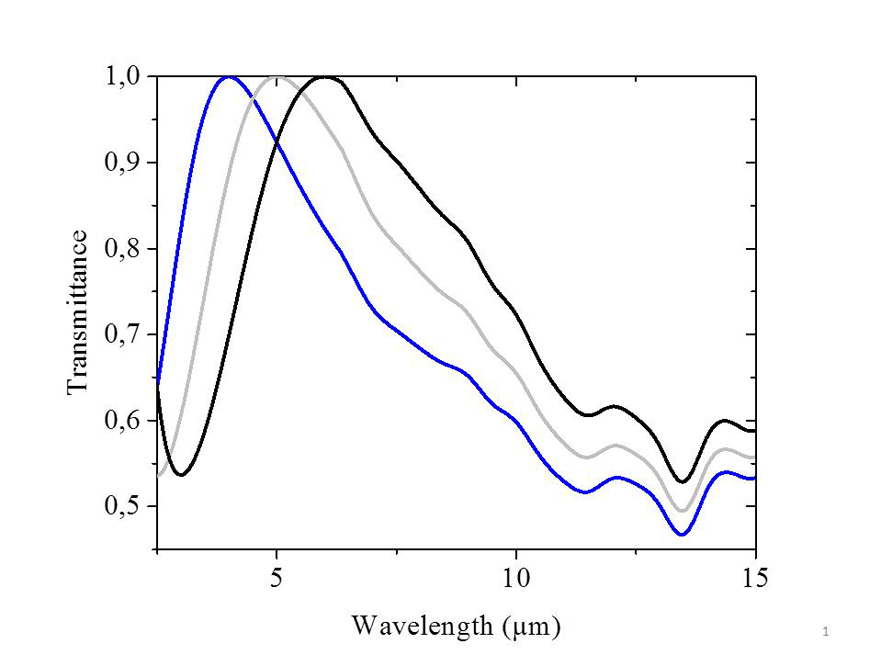
To optimally provide this area with application-specific IR imagers, adjustments must be made to the sensor element as well as the entrance window of the vacuum housing. On the entrance window the shifting of the transparency window can be adjusted to the respective application, for example. Apart from the entrance window, the optical construction of the sensor element can be adjusted to the requirements of the application as well.
The combination of equipment and know-how in CMOS and MEMS manufacturing at Fraunhofer IMS, which is unique in Germany, enables the development, design and manufacture of application-specific IR imagers (IRFPA). Since the entire uncooled infrared sensor, from the digital readout circuit to the microbolometer design to the vacuum housing, is developed and manufactured at the Fraunhofer IMS, changes and adaptations according to customer requirements are possible on almost all levels.
Examples of adaptations of uncooled infrared sensors as application-specific IR imagers
- Adaptation of the digital readout circuit (e.g. special frame rates, scene dynamic ranges or optical formats)
- Adjustment of the pixel pitch (e.g. in the range from 6 µm to 35 µm)
- Adaptation of spectral sensitivity (e.g. MWIR, LWIR, special cut-on or cut-off filters)
- Adaptation of the spectral transmission of the IR-transparent vacuum lid
- Adaptation of the microbolometer or the chip-scale package for harsh environments (e.g. high accelerations)