AIRISC Family – RISC-V processors for industry control, medical sensing, safety and many more
Profit from our SoC-design services:
- From concept and feasibility studies to the creation of complete designs and support
- Mixed signal system design based on RISC-V for smart sensors
- Development of FPGA-based and customer-specific ASIC solution
- Functional safety and cyber security for critical applications in the aerospace, automotive and industrial sectors
- Efficient hardware for inference and training of neural networks

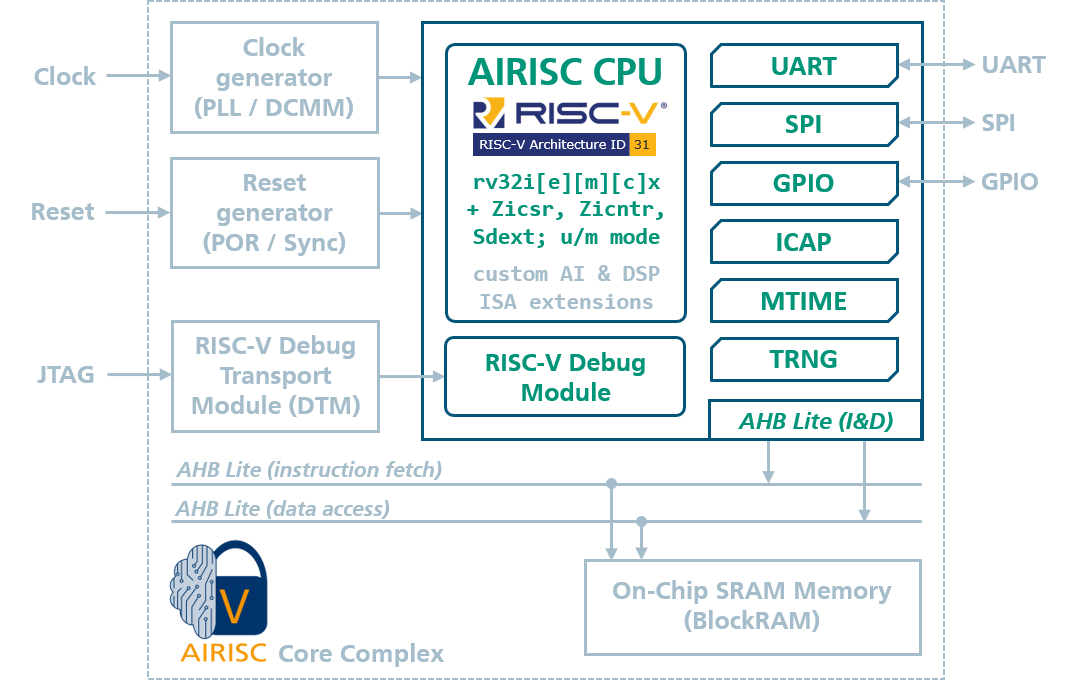
Trustworthy RISC-V cores
The AIRISC family of RISC-V cores developed by Fraunhofer IMS enables efficient machine learning and AI in sensors, IoT devices, and other embedded applications. AIRISC variants with extended safety mechanisms such as dual-core lock-stepping (DCLS) or error correcting codes (ECC) are available for use in fail-safe systems according to ISO 26262 (up to ASIL-D) and DIN 61508. Because intellectual property protection is very important in these applications, the AIRISC family provides cryptographic security features such as firmware protection and secure booting. The free RISC-V architecture makes it possible to implement customer-specific extensions in a short time and thus provides optimum computing performance for special applications. These features make AIRISC the best choice for real-time embedded sensor applications and integration into IoT systems.
Designed for Embedded AI
In interaction with the AIfES software library (AI for Emedded Systems) invented by Fraunhofer IMS, the AIRISC processor family supports the inference and training of neural networks directly on the embedded device. Integrated accelerators enable distributed training in networked devices (federated learning) and also the calibration of sensors using AI. Data processing directly in the sensor, without the need for permanent communication with the cloud, makes the AIRISC processor interesting for energy-autonomous and wearable sensor systems. It enables the design of compact privacy-preserving electronic systems and ISA extensions (Industry Standard Architecture).

AIRISC projects
Semiconductor chip with integrated AI can detect heart diseases
With almost two million people affected, atrial fibrillation is one of the most widespread diseases in Germany. AF that is often detected too late and can have fatal consequences for patients, such as a stroke. The severe consequences could be avoided by early intervention. With significant participation of the Fraunhofer IMS, the »ARTEMIS« consortium aims to provide efficient, digital healthcare for this disease. The main innovation consists of miniaturized ECG electronics based on artificial intelligence, which detects atrial fibrillation in real time directly on the patient.
Recording astronauts' stress profiles for safer flights into space: With the help of the AI-Suit sensor system, blood pressure can be measured in the space suit
In the future, more people will fly into space, who do not fit the physical profile of professional astronauts. For this, spacesuits will have to become even safer to monitor the physical strain on people. The Fraunhofer IMS has developed the AI-Suit system, which measures the wearer's vital parameters inside the spacesuit to monitor the stress level.

Easy to use and more efficient GaN power modules
In the »GaNext« project (short for next-generation GaN power modules), the aim is to lower the entry hurdle in the use of gallium nitride (GaN) semiconductors and at the same time improve the efficiency and compactness of GaN-based modules for power electronics. The project focuses on the development of an intelligent power module (IPM) based on GaN devices. These are combined with gate drivers and a programmable, fail-safe control unit with integrated protection circuits. The integration of the individual components in compact housing increases the end-user-friendliness.
More compact, efficient, and reliable power electronics for future technologies such as drones, electric aircraft, or collaborative medical robots
PowerCare implements a new monitoring concept in the form of a miniaturized motor controller with integrated real-time failure prediction, thus laying the foundation for a new evolutionary stage of intelligent power modules. For this purpose, AI-based prediction models are implemented on a domain-specific RISC-V control SoC combined with highly efficient GaN power transistors to form a power module.
This work was supported by the Fraunhofer Internal Programs under Grant No. PREPARE 40-06175.
Executing AI algorithms directly on the chip: Our RISC-V processor, AIRISC-POWER, enhances energy efficiency and reliability of power electronics systems
The Horizon KDT project R-PODID aims to increase the energy efficiency and reliability of power electronics systems and modules. This shall be realized by integrating artificial intelligence on embedded devices into the power module. The partners of the project will face the challenge from different angles:
- Investigation of specific AI algorithms and how to deploy them on resource-constrained devices
- Developing high-power semiconductor devices based on GaN and SiC (Silicon Carbide) technologies that meet the requirements of modern industry and e-mobility
- Using innovative sensors as well as packaging solutions to collect real-time data to be used as input to the AI models to improve the robustness of the power systems
Fraunhofer IMS adapts its AIRISC-POWER design within the project to be able to execute the AI algorithms directly on chip.
R-PODID is an EU project and is funded under the following number: 101112338 — R-PODID — HORIZON-KDT-JU-2022-2-RIA.
»ASIL-D ready« safety controller for an autonomous drone
Among the most efficient gliding birds is the albatross. The bird's terrific maneuverability and effortless hovering on air currents over thousands of kilometers are admirable. A consortium of six Fraunhofer institutes wants to take this phenomenon from nature and develop the ALBACOPTER®, a flying machine that not only hovers fantastically but can also take off and land efficiently.
Fraunhofer IMS has developed a safety controller for UAVs (Unmanned Aerial Vehicles), the AIRISC-SAFETY, which is certified »ASIL-D ready« (automotive safety integrity level). The RISC-V processor AIRISC from Fraunhofer IMS has been adapted to ensure the monitoring of the communication interfaces and the connection from the autonomous drone to the bus network.
Learn more about the AIRISC-SAFETY.
Learn more about the Fraunhofer Lighthouse Project ALBACOPTER®.
Research platform for »trustworthy electronics«
To use electronics safely and reliably, it must be possible to understand where they come from, what they do and how they are constructed. Currently, there are some technical solutions in the sense of trustworthy electronics, but there is not yet an end-to-end methodology for trustworthiness that sufficiently incorporates the entire value chain. This is the starting point of the Velektronik research project that started in March 2021.
Novel design methods for trustworthy electronic circuits
In the VE-DIVA-IC project, Fraunhofer IMS and Fraunhofer AISEC are working together with other partners to strengthen the protection of the integrity and identity with electronic components in the fields of mobility and automation technology. By taking an additional step in the design of integrated circuits, electronic components, for example in vehicles, can thus be secured in a trustworthy manner.
Sensor technology for contactless vital signs measurement to relieve the workload of care workers and alleviate the shortage of skilled workers
In the CAREFUL EDGE X project, Fraunhofer IMS is working with further partners to develop an intelligent solution for care that works by contactless recording and local processing of vital parameters via edge computing. In the project, the Fraunhofer IMS contributes the know-how for contactless sensor technology to record vital parameters in an intelligent nursing room. Together with other devices such as a nursing bed, a seat cushion and a nursing robot, the data will be validated and used to optimize care. Communication between the devices is handled via a digital care platform and software. The CAREFUL EDGE-X project therefore connects the fields of nursing, robotics and smart living and enables cross-sector use. Local data processing at the edge reduces energy consumption in cloud data centers, which benefits climate and environmental protection.
Watch the video to find out how our AI-based, contactless vital signs measurement can revolutionize care
Higher energy efficiencies and process optimizations for an industry in transition
Edge AIoT (Artificial Intelligence integrated in the Internet of Things) is not only a trend, but also increasingly necessary for our industry. More often, small devices need to process huge amounts of data close to the point of origin with low latency, while efficiently running AI algorithms. For this, solutions that process the data in the sensors themselves are already on the rise, but these require a comprehensive and innovative approach to minimize costs and power consumption. Therefore, in the context of industrial applications, continuous improvement of hardware for computing AI algorithms is needed. This challenge is addressed by 19 companies and universities in the context of the research project CLEVER. Their common goal is the development of an energy-efficient hardware accelerator for AI algorithms.
Implement AI on any hardware with AIfES®
With the open-source AI software framework AIfES® (Artificial Intelligence for Embedded Systems) you can run and even train artificial neural networks on virtually any hardware. Tiny embedded systems plus artificial intelligence - the topic of our time.
Learn more about AIRISC on Google Scholar.
/github-mark.png)