
In January 2017, the German government adopted a draft law allowing autonomous driving on German roads. As the number one car country, Germany should not only be the leading market for autonomous driving, but also the leading provider. Autonomous driving requires a wide variety of sensors for safe and reliable continuous detection of the environment, such as cameras in the VIS range, radar or ultrasonic systems, lidar systems and cameras in the far infrared range (FIR). The combination of several of these sensors (sensor fusion) ensures environmental detection even under difficult environmental conditions.
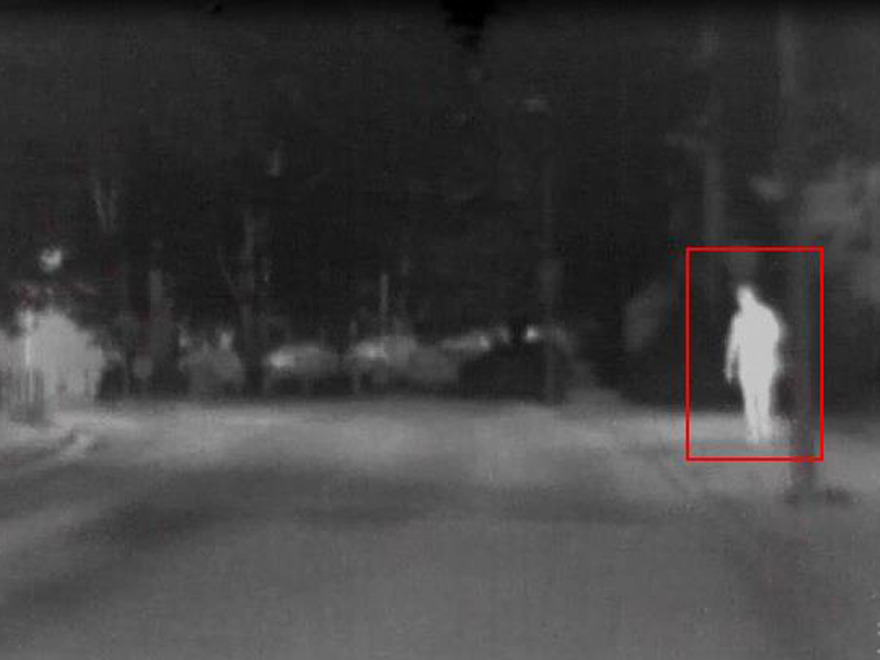
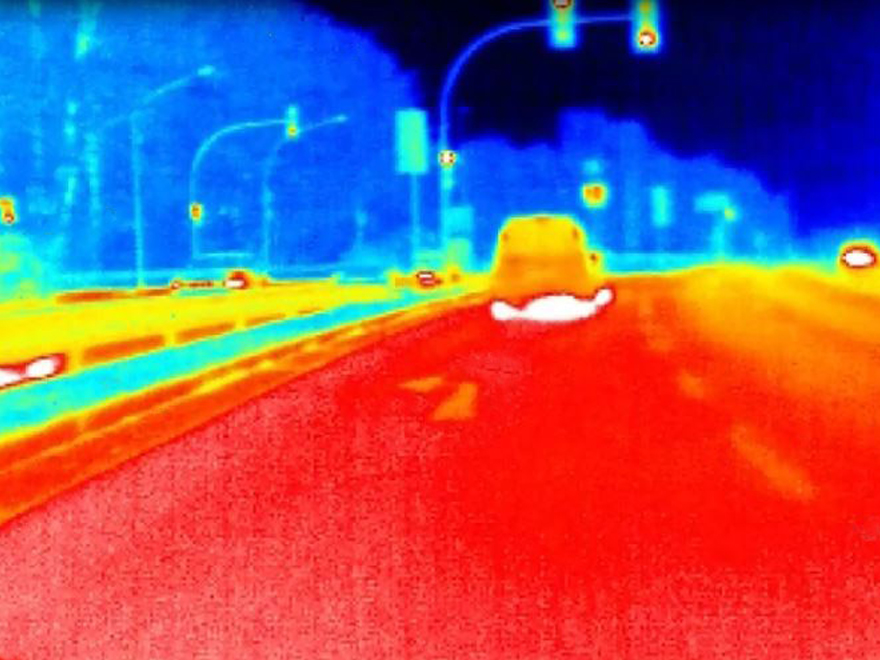
FIR cameras as imaging systems in particular benefit from the properties of "light" in the wavelength range from 8 µm to 14 µm due to a different physical detection principle than passive image sensors. They enable "seeing" even under difficult environmental conditions, such as tunnel entrances and exits, low sun, fog, smog or heavy rainfall. Under these conditions, the signal quality of cameras in the VIS range, but also of lidar systems, is greatly reduced, while FIR cameras deliver detailed images.
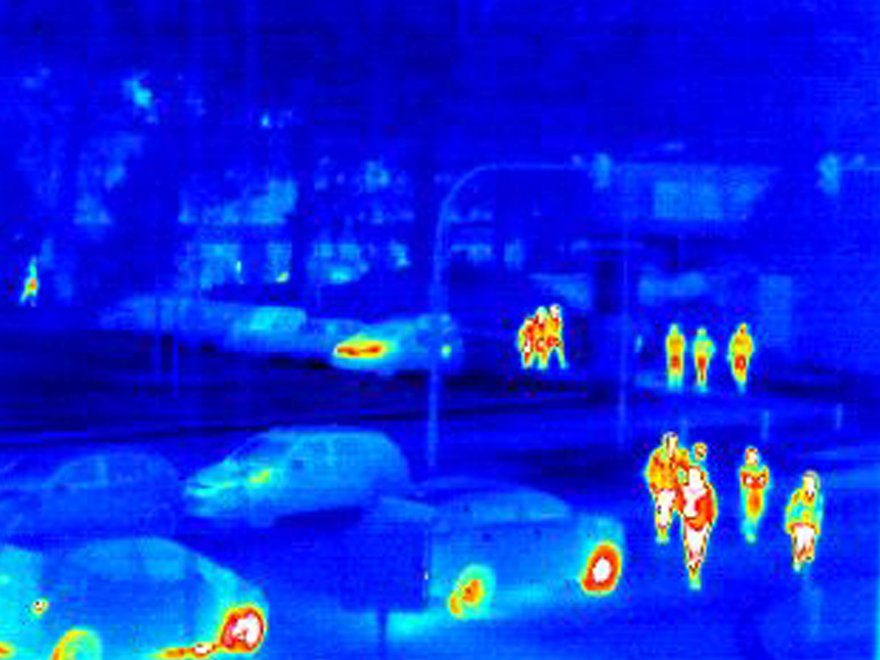
Studies show that even during the day, FIR cameras can match the quality of an optical sensor in terms of hits and error rate in the detection of humans or animals due to temperature contrast in clear and well-lit scenes. The use of FIR cameras in autonomous driving is almost indispensable in terms of safety. Another technical advantage of the FIR camera compared to other systems is the relatively small amount of data required for the evaluation of the system. This not only tends to make the evaluation faster, but also reduces the total amount of data to be transmitted into autonomous driving.
In addition, uncooled infrared sensors can reliably monitor traffic day and night. The thermal image of people, vehicles or other road users can be identified unambiguously and anonymously in accordance with data protection regulations. The technology works almost uninfluenced by weather conditions. An IR camera module can be used, for example, to control traffic lights or barriers more efficiently. Verification can also be performed during access controls or automatic electronic fee collection using uncooled infrared sensors.