Conventional CCD technologies for optical sensors are mainly used where high demands have to be met by the sensor:
- Applications that require an extremely low dark signal
- Applications with Time Delay Integration (TDI) (e.g. space detectors)
Usually, for this kind of sensors a highly pure, low-defect silicon material is used as a basis to minimize crystal defects as a cause for parasitic dark signals. The high dynamic range is achieved by operating voltages that allow more than 10 V differences in potential and therefore enable the transport of large charge packages.
One of the significant disadvantages of a CCD not integrated into a CMOS chip is that the complete signal processing as well as the sensor control has to be carried out externally. This leads to considerable parasitic effects, for example high line resistance or bond wire inductivities. Another disadvantage is that the pixel values need to be transferred over a very fast analog CCD shift register to the exit. The shift register produces high losses and therefore the power consumption for conventional CCDs are much higher than for the CMOS-CCDs.
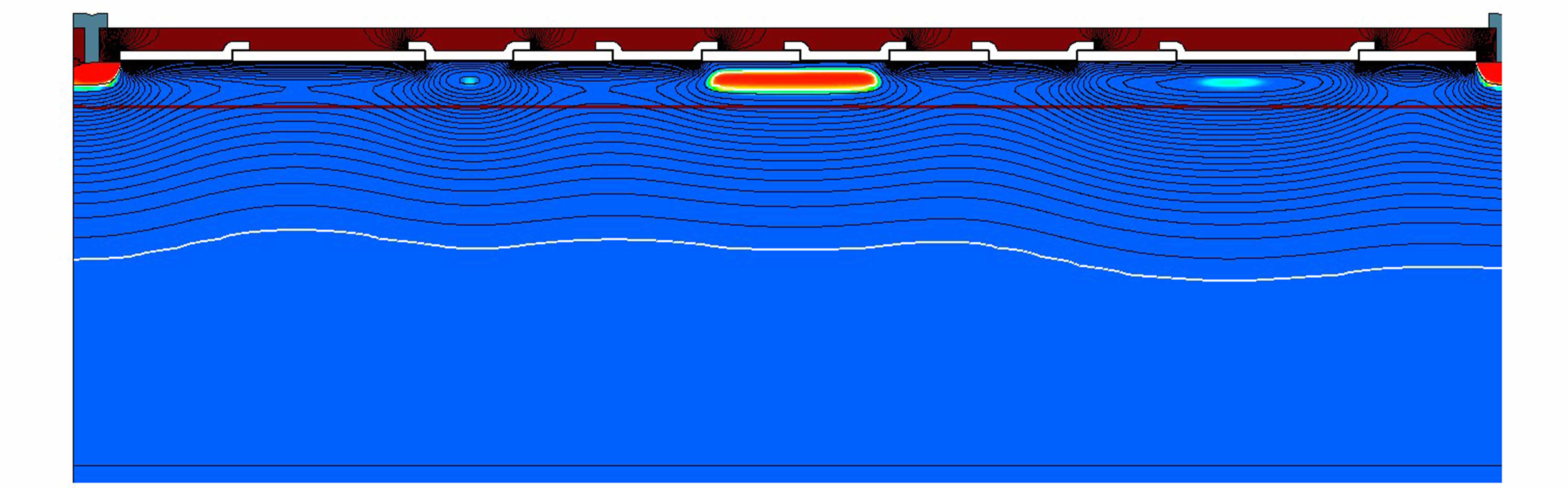
Fraunhofer IMS has developed a process in which CCDs are integrated into the CMOs process in a way that allows the CMOS-CCDs to use the advantages of both technologies:
- The integration of the CCD into the CMOS process enables the direct parallel signal processing and AD conversion on the chip and therefore minimizes the parasitic disruptive effects. The output of the digitized data is done over several channels which removes the bottleneck in data transfer.
- The adaption of the process to the voltages typically used in CCDs allows for the processing of big charge packages.
- A specially tailored gate structure from two overlapping polysilicon gates guarantees a continuous potential curve inside of the CMOS-CCD and enables a low-loss charge transport, especially for small signals.
- Through a deep channel implantation in the CMOS-CCD the charge transport is kept from the interface and therefore ensures a high transfer efficiency.
The main application area for the CMOS CCDs is in the field of TDI space detectors. For this application, sensors with very high optical requirements are needed, which at the same time have a low power consumption in order to keep the effort, the weight and thus the costs of the sensor low.