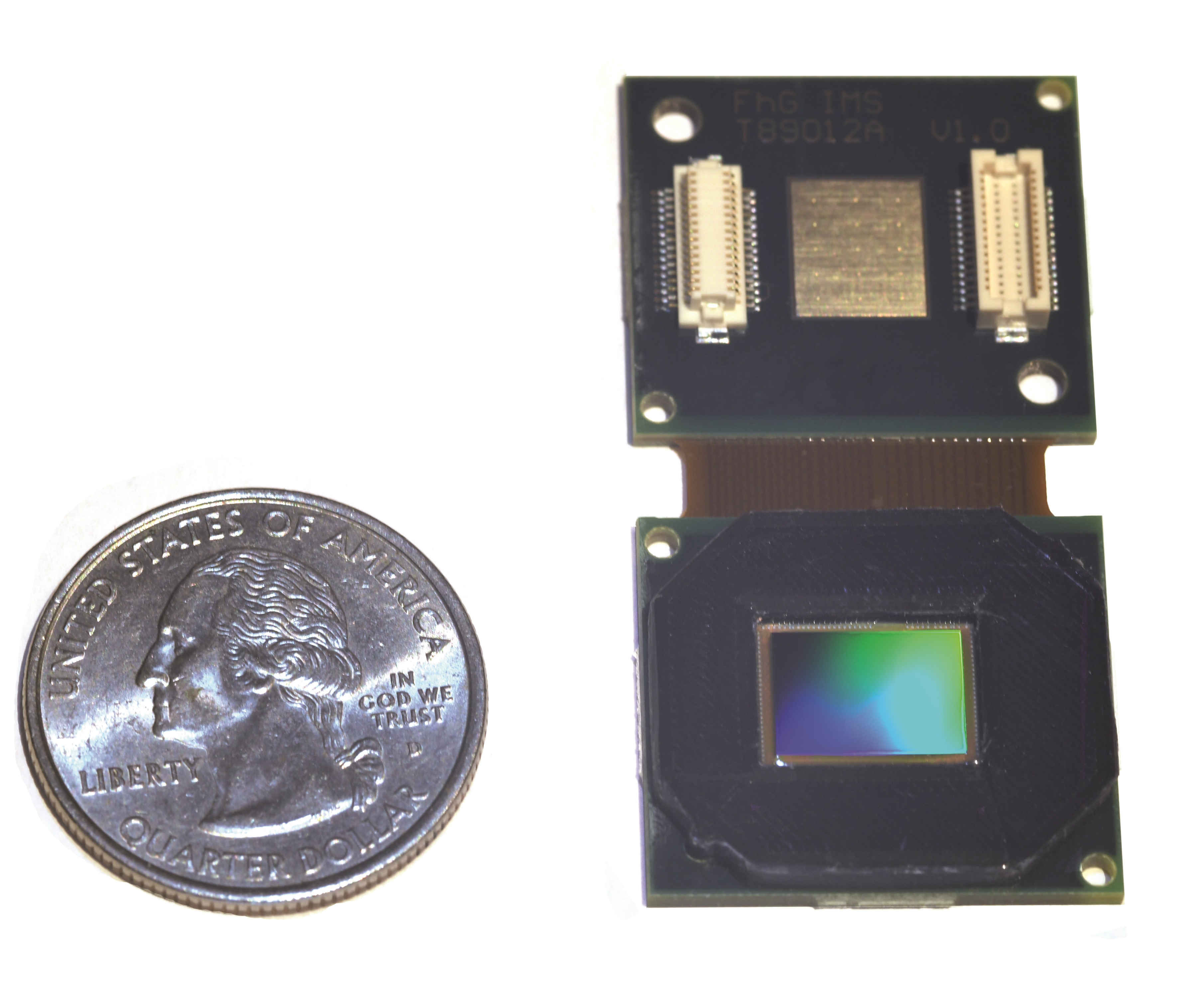
Fraunhofer IMS has developed a digital IRFPA with a QVGA resolution and 17 μm pixelpitch. The digital IRFPA allows for the detection of emitted thermal radiation in the MWIR area (wavelength 3 μm to 5 μm) or the LWIR area (wavelength 8 μm to 14 μm). Goal of the project was the development of a compact, efficient and easy to use IR imager.
Therefore, Fraunhofer IMS combined the microbolometer technology with a digital readout circuit and a chip-scale vacuum package. The microbolometer technology developed at Faunhofer IMS uses amorpous silicon and has a pixelpitch of 17 μm. A readout circuit has been developed for the readout of these microbolometers that converts the temperature-affected change in resistance into digital values through the parallel operation of a number of ΣΔ-ADCs. For the easy operation of the digital IRFPAthe readout circuit contains a SPI interface for the configuration of the IR imager and configurable internal voltage references for the ΣΔ-ADCs. The recorded temperature distribution is available in a 16-bit resolution. The compact construction has been realized through the development of a chip-scale vacuum package. Using this technology the surface of the digital IRFPA could be confined to the area needed by the readout circuit and a height of 1.5 mm could be reached.
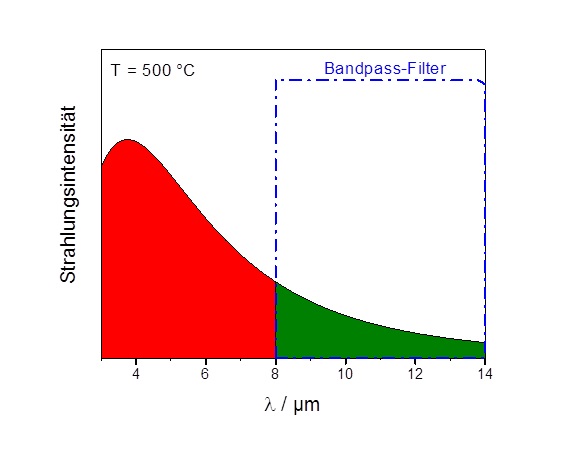
For contactless temperature measurements in process control uncooled IR image sensors (IRFPAs) based on microbolometers are used. If the objects to be examined show a high temperature (e. g. 300 °C to 1000 °C), standard IRFPAs can only be used for temperature measurement with great measurement errors, because they usually limit the IR spectral range through bandpass filters to l = 8 μm to l = 14 μm while the maximum of the radiation intensity for these temperatures is on significantly lower wavelengths (300 °C: 5.1 μm, 1000°C = 2.3 μm). Fraunhofer IMS goes without a bandpass filter on its digital 17 μm QVGA IRFPAs for these applications and optimized the anti-reflective layer for the wavelength range of 3 μm to 5 μm (MWIR). The latest generation of highly sensitive uncooled infrared sensors with 320 x 256 pixels for the LWIR and MWIR range enables a significantly increased temperature measurements with this adapted wavelength range. In the combination of the significantly extended spectral range with the high dynamics this new sensor stands out for the monitoring of high process temperatures.
The core properties of the digital IRFPA are:
- Uncooled infrared sensor for thermal measuring or imaging applications in the MWIR range (wavelength of 3 μm to 5 μm) or in the LWIR range (wavelength of 8 μm to 14 μm)
- Sensor technology: uncooled microbolometer (amorphous silicon)
- Optical resolution: 320 x 256 pixels (configurable)
- Line resolution of 4 to 256 lines digitally adjustable
- Column resolution: 240 columns (non-adjustable)
- Pixelpitch: 17 μm
- Temperature resolution: NETD<60 mK (f/1.0, 295 K, 30 Hz)
- Dynamics: ΔT > 300K (without deterioration of the NETD value)
- Integrated temperature sensors (analog and digital) for operating modes TEC-less and shutterless
- Direct 16-bit readout of microbolometers
- Low-noise microbolometer readout with low fixed pattern noise
- Vaccum housing: Miniaturized chip-scale package