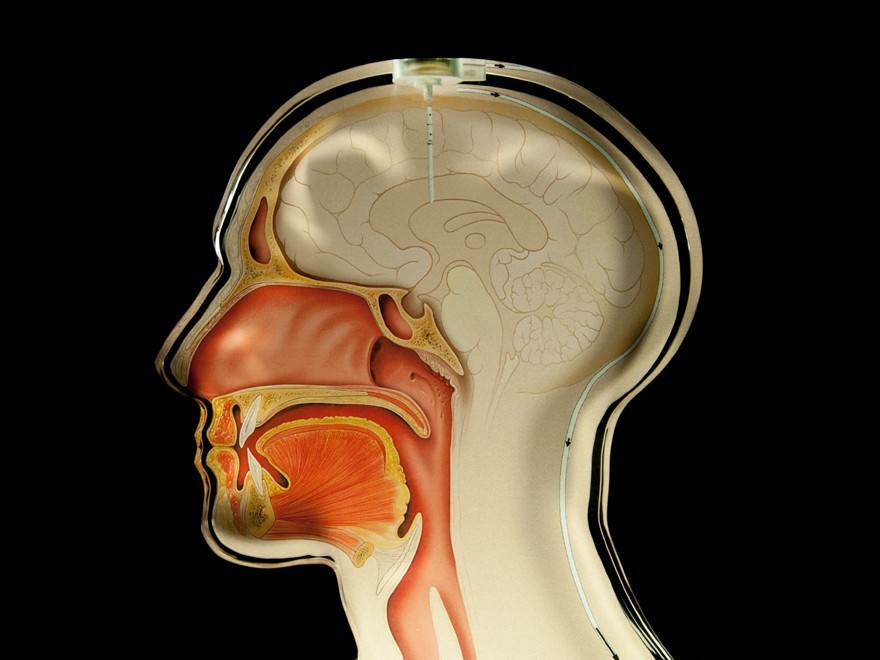
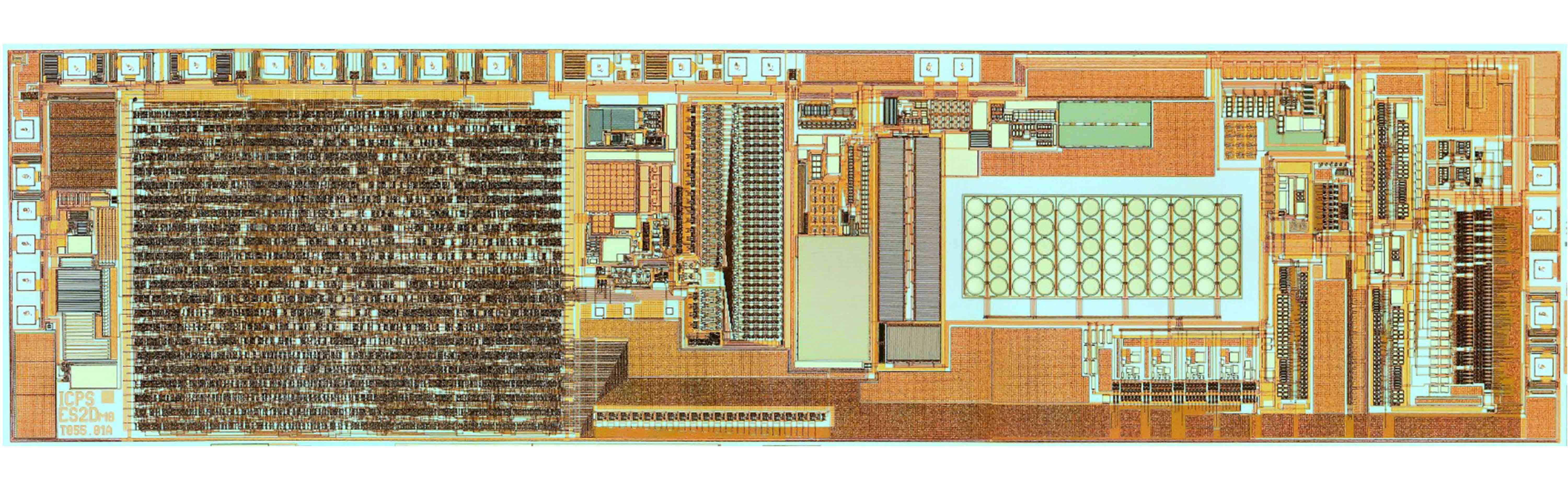
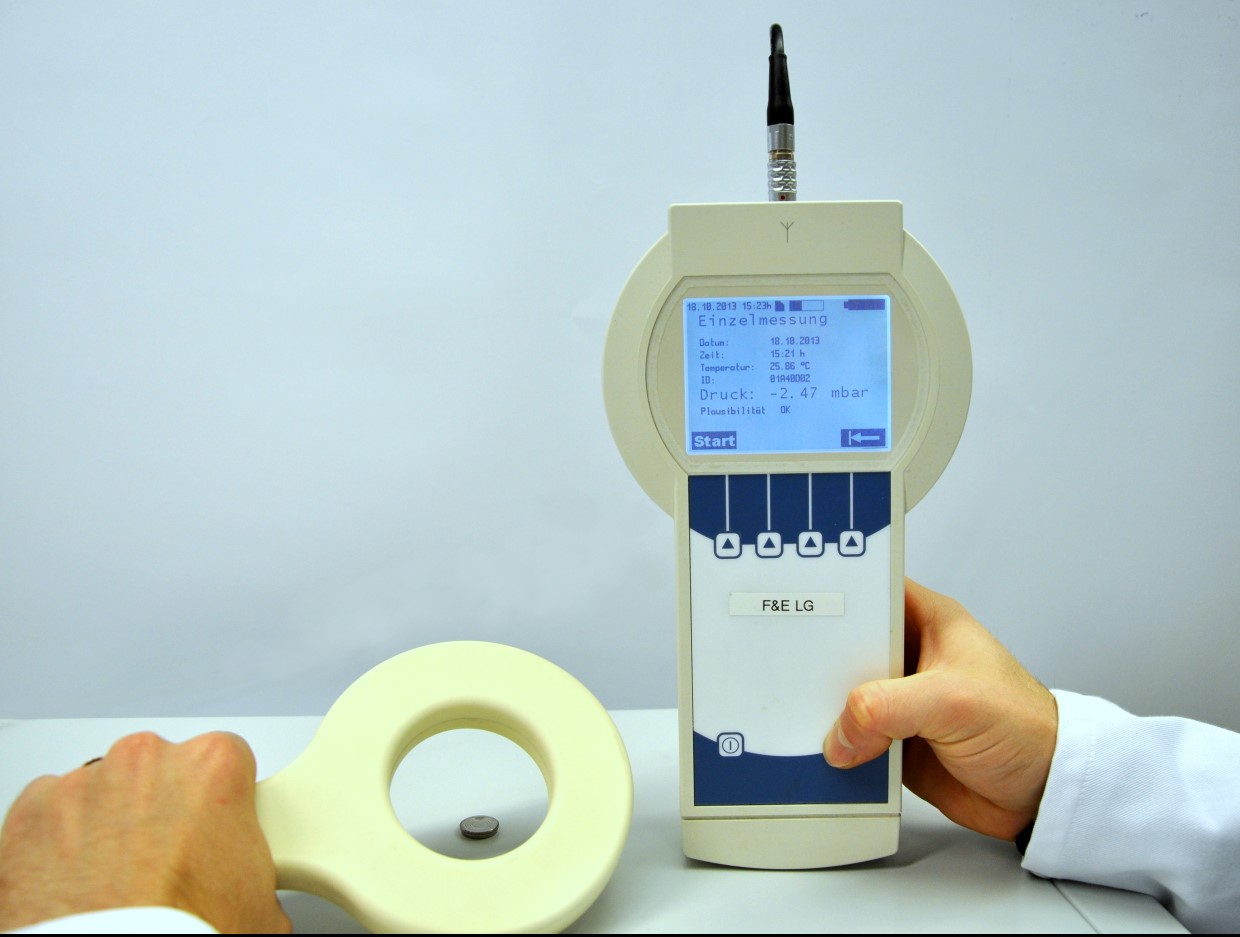
Pressure sensor for functional analysis in the brain shunt, a discharge system used for patients with increased intracranial pressure.
Pathological excess pressure in the brain has serious consequences for the patient. When diagnosed with hydrocephalus, the brain either produces too much cerebrospinal fluid or is unable to "break it down" sufficiently. As a result, the pressure in the head increases too much, causing damage to the brain. The remedy is a shunt system that doctors implant in the patient's brain. There, it drains excess fluid into the abdominal cavity, for example.